
This variance is unfavorable for Jerry’s Ice Cream becauseactual costs of $100,000 are higher than expected costs of$94,500. There are many costs that occur during production that it can be hard to track them all. Variable overhead is typically aggregated into the cost of goods sold, and so is not shown separately in the income statement. However, it may be listed as a separate line item in the cost of goods manufactured schedule, which is internal to the accounting department; it is not included in a company’s financial statements. This not only helps you run your business more effectively but is instrumental in making a budget. Knowing how much money you need to set aside for manufacturing overhead will help you create a more accurate budget.
- First, identify the manufacturing expenses in your business for a given period.
- Fixed overhead costs are costs that do not change even while the volume of production activity changes.
- It’s added to the cost of the final product, along with direct material and direct labor costs.
- There are a few business expenses that remain consistent over time, but the exact amount varies, based on production.
Variable Overhead Costs
The variable overhead spending concept is most applicable in situations where the production process is tightly controlled, as is the case when large numbers of identical units are produced. Often, explanation of this variance will need clarification from the production supervisor. Another variable overhead variance to consider is the variable overhead efficiency variance.
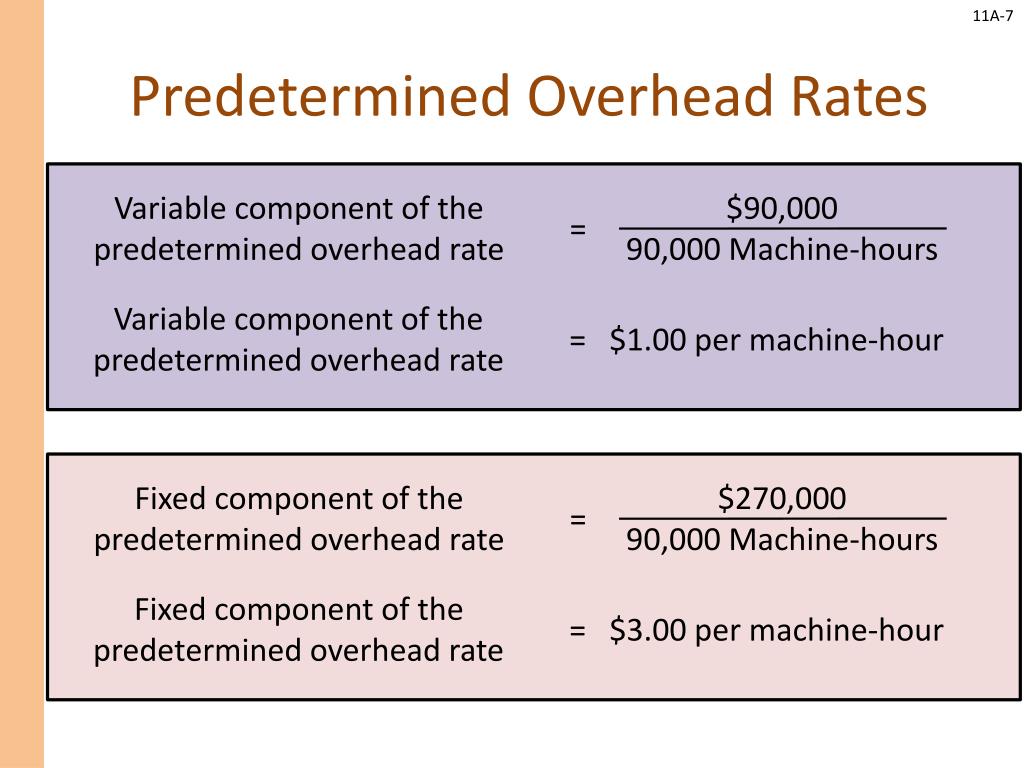
Importance of Calculating Variable Overheads
Variable manufacturing overhead includes a variety of indirect costs that vary with production volume. These costs are not directly attributable to specific units of product but are necessary for the production process. Examples include indirect materials, such as lubricants and cleaning supplies used in the machinery.
Identify Manufacturing Overhead Costs
Let’s define manufacturing overhead, look at the manufacturing overhead formula and how to calculate manufacturing overhead. The controller of a small, closely heldmanufacturing company embezzled close to $1,000,000 over a 3-yearperiod. With annual revenues of $30,000,000 and less than 100employees, the company certainly felt the impact of losing$1,000,000.
Determination of Variable Overhead Rate Variance
Sometimes these are obvious, such as office rent, but sometimes, you may have to dig deeper into your monthly expense reports to understand what’s happening. Cost behavior refers to the way in which a cost changes in relation to changes in the level of business activity or volume of production. As a result of the fluctuation, variable overheads can prove tough to evaluate and budget for accurately.
Manufacturing Overhead Budget Example
Variances in variable manufacturing overhead are classified as either a spending variance or an efficiency variance. Unfavorable spending variances occur when the factory purchases items at a higher rate than expected. For example, if the cost of a kilowatt of electricity went up or if a purchaser had to pay more on machine supplies than usual, there could be a spending variance.
Accurately calculating your company’s manufacturing overhead costs is important for budgeting. Including only direct or “operational” expenses in your financial plan can leave the company in a major cash crunch, as every business in every industry has to incur some overhead costs. Calculating these beforehand can help you plan better and reduce unexpected expenses. Variable overhead costs are costs that change as the volume of production changes or the number of services provided changes. Variable overhead costs decrease as production output decreases and increase when production output increases.
Now let’s assume that the actual cost for the variable manufacturing overhead (electricity and manufacturing supplies) during January was $90. Calculating your monthly or yearly manufacturing overhead can help you improve your company’s financial plan and find ways to budget for such expenses. Companies with effective strategies to calculate and plan for manufacturing overhead costs tend to be more prepared for business emergencies than businesses that never consider overhead expenses.
The standard overhead rate is the total budgeted overhead of \(\$10,000\) divided by the level of activity (direct labor hours) of \(2,000\) hours. Notice that fixed overhead remains constant at each of the production levels, but variable overhead changes based on unit output. If Connie’s Candy only produced at \(90\%\) capacity, for example, they should expect total clarity on the classification of account overhead to be \(\$9,600\) and a standard overhead rate of \(\$5.33\) (rounded). If Connie’s Candy produced \(2,200\) units, they should expect total overhead to be \(\$10,400\) and a standard overhead rate of \(\$4.73\) (rounded). In addition to the total standard overhead rate, Connie’s Candy will want to know the variable overhead rates at each activity level.
While we have many project views, the kanban board contains key details on how much you’re spending on production. Use it to centralize manufacturing processes and collaborate with your team so you know how much you’re spending during production. Explore the intricacies of variable manufacturing overhead, including its elements, cost implications, and effective management strategies for businesses.


